Entering university marks a significant milestone in a young adult’s life, often representing the first time they experience independence away from the comforts of home. While this transition is exciting, it can also be daunting, particularly when it comes to managing finances.
For many students, this period is not only about academic growth but also about navigating the complexities of budgeting, saving, and spending wisely. Financial literacy becomes crucial during this time, as students must learn to balance their educational expenses with personal needs and desires.
Managing finances effectively while in university is essential for several reasons. Firstly, many students face the challenge of living on a limited budget, often relying on part-time jobs, student loans, or parental support. Without proper financial management skills, it is easy to fall into debt or overspend on non-essential items.
According to Investopedia, establishing a self-enforced budget is one of the most effective ways for college students to manage their money and avoid financial pitfalls[1]. By tracking income and expenses, students can make informed decisions about how to allocate their funds.
Moreover, understanding the difference between needs and wants is vital for effective financial management. Students often encounter various discretionary expenses such as entertainment, dining out, and shopping.
While these activities can enhance the university experience, they can also lead to financial strain if not managed properly. Learning to prioritize essential purchases—such as tuition, housing, and textbooks—over non-essential ones will help students maintain financial stability throughout their academic journey.
Another critical aspect of managing finances as a university student is the importance of saving. Establishing a savings habit early on can provide a safety net for unexpected expenses and help students prepare for future financial goals. Whether it’s setting aside funds for emergencies or planning for post-graduation expenses, cultivating the discipline to save can lead to greater financial security. Opening a savings account that earns interest can also serve as an incentive for students to save more consistently.
In addition to budgeting and saving, students should also seek out economic ways to purchase essential items and supplies. Utilizing student discounts, shopping during sales, or buying second-hand textbooks are practical strategies that can significantly reduce expenses. Furthermore, sharing costs with roommates—such as splitting grocery bills or sharing subscription services—can lead to substantial savings over time.
As students navigate their financial responsibilities, they should also be mindful of the long-term implications of their financial decisions. Understanding concepts such as credit scores and debt management is crucial for maintaining financial health beyond university life. Poor financial habits developed during this time can have lasting effects on future opportunities, including securing loans for further education or purchasing a home.
Ultimately, managing finances as a university student requires a combination of planning, discipline, and adaptability. By setting clear financial goals and regularly reviewing their budgets, students can develop healthy financial habits that will serve them well throughout their lives. The skills learned during this formative period are invaluable; not only do they contribute to academic success by alleviating financial stress, but they also lay the foundation for responsible financial behavior in adulthood.
In conclusion, while university life presents numerous challenges—financial management should not be overlooked. By prioritizing budgeting, saving, and making informed spending decisions, students can navigate their finances effectively and enjoy their educational experience without unnecessary stress. As they embark on this exciting journey toward independence, equipping themselves with the knowledge and skills necessary for sound financial management will empower them to thrive both academically and personally.
Understanding Your Financial Aid
Navigating the financial aid landscape at Boston University (BU) can be a crucial part of ensuring that students can afford their education while minimizing debt. Financial aid is designed to help students cover the costs of tuition, fees, room, board, and other educational expenses. At BU, various types of financial aid are available, including scholarships, grants, and loans, each with unique eligibility criteria and application processes. Understanding these options and how to manage them effectively is essential for maximizing financial support during your university experience.
Types of Financial Aid Available at Boston University
Scholarships
Boston University offers a range of scholarships that cater to different student needs and achievements. These include:
- Need-Based Scholarships: These scholarships are awarded based on demonstrated financial need as determined by the information provided in the FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid) and CSS Profile™. Notable examples include the BU Need-Based Scholarship and the BU Community Service Award, which supports students from Boston public high schools.
- Merit-Based Scholarships: While BU primarily focuses on need-based aid, there are merit-based scholarships available for students who demonstrate exceptional academic performance or other talents.
Grants
Grants are another vital component of financial aid at BU. Unlike loans, grants do not require repayment. Key grant options include:
- Federal Pell Grant: Awarded to undergraduate students who demonstrate substantial financial need. Eligibility is determined through the FAFSA.
- Federal Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grant (SEOG): This grant provides additional assistance to students with exceptional financial need, typically those who qualify for the Pell Grant.
Loans
Loans are a common form of financial aid that must be repaid after graduation or when enrollment ends. At BU, students may consider:
- Federal Direct Subsidized Loans: These loans are available to students with demonstrated financial need and do not accrue interest while the student is enrolled at least half-time.
- Federal Direct Unsubsidized Loans: Available to all students regardless of financial need, these loans begin accruing interest immediately upon disbursement.
- Private Loans: Students may also explore private loan options through banks or credit unions; however, these often come with higher interest rates and less favorable repayment terms compared to federal loans.
Tips on Managing Financial Aid Packages
Managing financial aid packages effectively requires organization and understanding of loan terms. Here are some tips for BU students:
- Stay Organized: Keep all financial aid documents in one place, including award letters, loan agreements, and communications from the financial aid office. Consider using digital tools or apps to track deadlines and required documents.
- Understand Loan Terms: Before accepting any loans, thoroughly review the terms and conditions, including interest rates, repayment plans, and grace periods. This knowledge will help you make informed decisions about borrowing.
- Regularly Review Your Financial Aid Status: Use the MyBU Applicant Portal to monitor your financial aid status and ensure that you meet all requirements for maintaining your awards. This includes keeping a cumulative GPA above 2.0 and completing at least 75% of attempted courses.
Maximizing Financial Aid Opportunities at BU
To make the most of available financial aid opportunities at Boston University:
- Apply Early: Complete your FAFSA and CSS Profile as early as possible to maximize your chances of receiving need-based aid. Pay attention to application deadlines to ensure you don’t miss out on potential funding.
- Utilize Financial Aid Resources: Take advantage of resources offered by BU’s Financial Assistance office, including workshops on budgeting and managing debt. These resources can provide valuable insights into making informed financial decisions.
- Explore Additional Scholarships: In addition to institutional scholarships, search for external scholarships from organizations, foundations, and community groups. Websites like Fastweb or Cappex can help identify opportunities that match your profile.
General Financial Aid Tips for University Students
Understanding how to apply for financial aid effectively is crucial for all university students:
- Steps to Apply:
- Complete the FAFSA annually.
- Submit the CSS Profile if required by your institution.
- Keep track of deadlines for applications and required documents.
- Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Failing to apply early or missing deadlines can limit your eligibility for aid.
- Not reviewing loan terms before accepting them can lead to unexpected debt burdens post-graduation.
- Underestimating living expenses or additional costs can result in budget shortfalls.
- Importance of Meeting Deadlines: Timely submission of applications is critical in securing financial aid. Many programs have limited funding available on a first-come, first-served basis; therefore, meeting deadlines ensures you maximize your potential aid package.
In conclusion, understanding your financial aid options at Boston University is essential for navigating university expenses effectively. By familiarizing yourself with available scholarships, grants, and loans—and employing strategic management techniques—you can make informed decisions that enhance your educational experience while minimizing financial stress. Taking proactive steps in managing your finances will not only support your academic journey but also lay a solid foundation for your future financial well-being.
Budgeting for University Life
Managing finances effectively is crucial for university students, as it directly impacts their academic experience and overall well-being. Creating a practical and realistic budget can help students navigate the financial challenges of university life, ensuring they cover essential expenses while also enjoying their time on campus. This guide will provide insights into how to create a budget, manage living expenses, and set financial goals that align with both short-term needs and long-term aspirations.
Creating a Practical and Realistic Budget
The first step in effective budgeting is to assess your income and expenses. Begin by listing all sources of income, which may include:
- Student loans: Federal or private loans that help cover tuition and living costs.
- Scholarships and grants: Financial aid that does not need to be repaid.
- Part-time job earnings: Income from work-study programs or part-time employment.
- Parental support: Any financial assistance received from family members.
Once you have a clear picture of your income, it’s essential to identify your expenses. Categorize them into two main groups: fixed expenses (tuition, rent, utilities) and variable expenses (groceries, entertainment, personal spending). This categorization will help you understand where your money goes each month.
Essential Expenses
Prioritize essential expenses in your budget. These typically include:
- Tuition fees: The cost of classes and educational materials.
- Rent: Monthly housing costs, whether on-campus or off-campus.
- Utilities: Electricity, water, internet, and other necessary services.
- Food: Grocery shopping and meal plans.
- Transportation: Costs related to commuting to campus or travel.
Discretionary Spending
Once you’ve accounted for your essential expenses, allocate funds for discretionary spending. This category includes entertainment, dining out, clothing, and other non-essential items. It’s important to set limits on this spending to avoid overspending.
Tips on Managing Living Expenses
- Meal Planning: One of the largest variable expenses for students is food. Plan meals for the week and create a shopping list based on this plan. Cooking at home can significantly reduce food costs compared to eating out.
- Use Student Discounts: Many retailers offer discounts for students. Always carry your student ID and inquire about discounts when shopping for clothes, electronics, or dining out.
- Public Transportation: Utilize public transportation options or consider biking to save on fuel and parking costs. Many universities offer discounted transit passes for students.
- Rent Wisely: If living off-campus, consider sharing an apartment with roommates to split rent and utility costs. This can lead to substantial savings compared to living alone.
- Buy or Rent Used Textbooks: Textbooks can be expensive; consider buying used books or renting them through online platforms. Additionally, explore digital versions which are often cheaper than physical copies.
Setting Financial Goals
Establishing financial goals is vital for maintaining focus on both short-term needs and long-term aspirations:
Short-Term Goals
Short-term goals might include managing semester expenses effectively or saving for specific purchases like textbooks or a laptop. To achieve these goals:
- Create a savings plan that allocates a portion of your monthly budget toward these expenses.
- Use any extra income from part-time jobs or refunds from financial aid to boost your savings.
Long-Term Goals
Long-term financial goals could involve saving for graduation-related expenses such as job search costs or further education. To prepare for these goals:
- Emergency Fund: Aim to build an emergency fund that covers at least three months’ worth of living expenses. This fund can provide peace of mind in case of unexpected costs.
- Career Preparation: Consider setting aside funds for career-related expenses like resume workshops, professional attire for interviews, or networking events.
- Debt Management: If you have student loans, familiarize yourself with repayment options early on. Understanding loan terms can help you make informed decisions about borrowing and repayment strategies.
Managing Student Loans and Debts
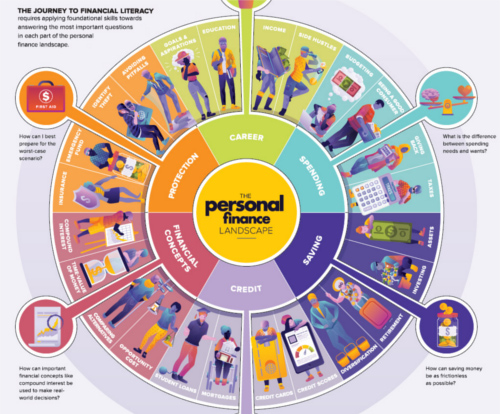
Student loans have become a fundamental aspect of financing higher education for many students, providing the necessary funds to cover tuition, living expenses, and other educational costs. However, with the opportunity to borrow comes the responsibility of managing that debt effectively. Understanding the types of loans available, the importance of responsible management, and strategies for repayment can significantly impact a student’s financial future.
Overview of Student Loans
Student loans can be broadly categorized into federal and private loans. Federal student loans typically offer lower interest rates and more flexible repayment options compared to private loans. They include Direct Subsidized Loans, which are based on financial need and do not accrue interest while the student is enrolled at least half-time, and Direct Unsubsidized Loans, which are available regardless of need but begin accruing interest immediately. Private loans, on the other hand, are offered by banks or credit unions and often come with higher interest rates and less favorable repayment terms.
Managing student loans responsibly is crucial for maintaining financial stability after graduation. Failure to manage these debts can lead to long-term financial consequences, including damaged credit scores and increased stress levels. Therefore, it is essential for students to understand their loan agreements fully, including interest rates, repayment schedules, and any potential penalties for late payments.
Tips for Handling Loan Repayment Schedules
Students at institutions like Boston University (BU) and the University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin) can benefit from specific strategies tailored to their financial situations:
- Understand Your Loan Terms: Before entering repayment, familiarize yourself with the details of your loans. Know the total amount borrowed, interest rates, grace periods, and repayment options available. This understanding will help you make informed decisions about how to manage your payments.
- Create a Budget: Incorporate your loan repayments into your monthly budget. Assess your income sources—such as part-time jobs or stipends—and allocate funds for loan payments alongside essential living expenses like rent and groceries. A well-structured budget will help ensure you can meet your repayment obligations without falling behind.
- Explore Repayment Options: Federal loans offer various repayment plans, including standard repayment, graduated repayment, and income-driven repayment plans. Investigate which option best suits your financial situation. For example, income-driven plans adjust your monthly payment based on your income level, making them more manageable during times of financial difficulty.
- Consider Loan Deferment or Forbearance: If you encounter financial hardship after graduation, you may qualify for deferment or forbearance on federal student loans. These options allow you to temporarily postpone payments without defaulting on your loan. However, be aware that interest may continue to accrue during this period.
- Make Timely Payments: Consistency in making payments is key to managing student debt effectively. Setting up automatic payments can help ensure you never miss a due date while potentially qualifying you for an interest rate reduction from some lenders.
Pros and Cons of Taking Out Loans
While student loans can provide essential funding for education, they come with both advantages and disadvantages:
Pros:
- Access to Education: Loans enable students to pursue higher education that may otherwise be financially out of reach.
- Building Credit History: Responsible management of student loans can help establish a positive credit history, which is beneficial for future borrowing needs.
- Potentially Low Interest Rates: Federal loans often have lower interest rates compared to private alternatives.
Cons:
- Debt Burden: Accumulating debt can lead to significant financial stress post-graduation.
- Interest Accrual: Depending on the type of loan, interest may accumulate while in school or during deferment periods.
- Limited Flexibility: Some private loans may have strict repayment terms that limit options for borrowers facing financial difficulties.
Finding Ways to Minimize Debt
To minimize debt while pursuing higher education:
- Apply for Scholarships and Grants: Seek out scholarships and grants that do not require repayment. Many organizations offer funding based on merit or need; applying widely can reduce reliance on loans.
- Work Part-Time: Consider taking on a part-time job during school to help cover living expenses without needing additional loans.
- Live Frugally: Adopt a frugal lifestyle by budgeting carefully and avoiding unnecessary expenses. This approach can help save money that can be put toward tuition or loan repayments.
- Pay More Than the Minimum: Whenever possible, pay more than the minimum required payment on your loans. This strategy reduces the principal balance faster and decreases the overall amount of interest paid over time.
- Consider Refinancing After Graduation: Once you have established a steady income post-graduation, consider refinancing your student loans at a lower interest rate if eligible. This option can lower monthly payments and reduce total interest costs over time.
Finance Associations and Networking Opportunities
University finance associations play a crucial role in bridging the gap between academic learning and professional practice for students pursuing careers in finance. One such organization is the University Finance Association (UFA) at the University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin). These associations provide invaluable resources, networking opportunities, and practical experiences that enhance students’ understanding of financial concepts and prepare them for successful careers in the finance industry.
The Role of University Finance Associations
The University Finance Association at UT Austin is dedicated to enriching students’ educational experiences by supplementing classroom learning with real-world insights. The UFA organizes events that connect students with finance professionals, offering a platform for mentorship and networking.
Through guest speaker sessions, workshops, and panel discussions, members gain exposure to various career paths within finance, including corporate finance, investment banking, and financial analysis. This direct interaction with industry experts allows students to ask questions, seek advice, and gain insights into the skills needed to succeed in the competitive finance landscape.
In addition to networking opportunities, the UFA provides resources that help students develop essential skills relevant to their future careers. For example, members may participate in case competitions that challenge them to solve complex financial problems, enhancing their analytical and problem-solving abilities. These experiences not only bolster resumes but also foster teamwork and communication skills—key attributes sought by employers.
Getting Involved and Attending Events
Students interested in joining the University Finance Association can typically sign up through the organization’s website or during campus involvement fairs. Once involved, members are encouraged to actively participate in events and initiatives organized by the association.
To maximize their experience:
- Attend Workshops and Seminars: Regularly attending workshops hosted by the UFA helps students stay informed about current trends in finance and develop practical skills.
- Network with Alumni: Engaging with alumni who have successfully transitioned into finance careers can provide valuable insights and potential job leads.
- Participate in Case Competitions: Joining case competitions not only enhances problem-solving skills but also allows students to showcase their talents to potential employers.
- Utilize Online Platforms: Many associations maintain active social media profiles or online forums where members can connect, share resources, and stay updated on upcoming events.
Other University Finance Associations
Similar organizations exist at other universities, providing comparable benefits to students pursuing finance-related careers. For instance:
- Boston University (BU): The Boston University Finance & Investment Club is dedicated to helping students enhance their knowledge of finance and investment strategies. This club organizes workshops, speaker events, and networking opportunities with industry professionals.
- University of Michigan: The Michigan Business Women’s group includes a finance division that focuses on empowering women in finance through mentorship programs, networking events, and skill-building workshops.
- University of Southern California (USC): The USC Marshall School of Business has a Finance Association that connects students with professionals through networking events, guest lectures, and career development workshops.
These associations not only help students build valuable finance-related skills but also facilitate connections with industry professionals who can guide them as they navigate their career paths.
The Importance of Financial Literacy for University Students
Financial literacy is an essential skill for university students, equipping them with the knowledge and tools necessary to manage their finances effectively. As students transition into adulthood, they face numerous financial responsibilities, including tuition payments, living expenses, and the management of student loans. Understanding basic financial principles can significantly impact their ability to navigate these challenges, avoid common pitfalls, and plan for a secure financial future.
Understanding Basic Financial Principles
At its core, financial literacy encompasses a range of skills and knowledge that enable individuals to make informed financial decisions. For university students, this includes understanding how to budget, save, manage debt, invest wisely, and recognize financial scams. By grasping these concepts, students can establish good financial habits that will benefit them throughout their lives.
Budgeting and Saving
One of the most critical components of financial literacy is the ability to create and maintain a budget. A well-structured budget helps students track their income and expenses, ensuring they live within their means. By learning to budget effectively, students can allocate funds for essential expenses such as rent, groceries, and tuition while also setting aside money for savings. This practice not only prevents overspending but also fosters a sense of financial security.
Moreover, saving money—no matter how small the amount—can help students prepare for unexpected expenses or emergencies. Establishing a habit of saving early on lays the groundwork for future financial stability.
Debt Management
Many university students rely on student loans to finance their education. Understanding how to manage this debt is crucial for avoiding financial pitfalls post-graduation. Financial literacy teaches students about interest rates, repayment plans, and the importance of making timely payments. By comprehending these concepts, students can avoid falling into debt traps and maintain a good credit score—an essential factor for future borrowing needs such as mortgages or car loans.
Investment and Retirement Planning
Financial literacy also includes knowledge about investing and planning for retirement. Students who understand the basics of investing can make informed decisions about where to allocate their money for growth. Learning about different investment vehicles—such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds—can help students build wealth over time. Additionally, understanding the significance of starting retirement savings early can have a profound impact on their long-term financial health.
Avoiding Financial Scams
In today’s digital age, financial scams are prevalent and can easily target unsuspecting students. Financial literacy equips students with the skills needed to identify potential scams and protect themselves from fraud. By learning how to recognize warning signs—such as unsolicited offers or too-good-to-be-true investment opportunities—students can safeguard their finances against exploitation.
Benefits of Financial Literacy Education
Taking personal finance courses, attending workshops, or reading finance-related books can provide significant benefits for university students:
- Enhanced Financial Decision-Making: Courses in personal finance offer structured education on budgeting, saving, investing, and debt management. This knowledge empowers students to make informed choices that align with their financial goals.
- Improved Financial Behavior: Research indicates that students who receive financial education tend to save more money, make better spending decisions, and have higher credit scores than those who do not receive such training.
- Increased Confidence: Gaining financial knowledge boosts students’ confidence in managing their finances. This confidence can lead to more proactive behaviors regarding budgeting and investing.
- Long-Term Financial Security: By understanding how to manage money effectively during university years, students are better prepared for financial independence after graduation. They are equipped with the skills necessary to navigate the complexities of adult financial responsibilities.
Saving and Investing as a Student
Managing finances as a university student can be challenging, especially when balancing tuition, living expenses, and social activities. However, starting to save and invest—even on a small budget—can set the foundation for long-term financial health. Understanding how to effectively manage savings and investments can empower students to make informed financial decisions that will benefit them throughout their lives.
How University Students Can Start Saving and Investing
Opening a Savings Account
The first step in building a financial foundation is to open a savings account. A high-yield savings account is an excellent option for students, as it typically offers better interest rates than traditional savings accounts. This allows students to earn interest on their deposits while keeping their money accessible for emergencies or future expenses. When choosing a savings account, students should consider factors such as fees, minimum balance requirements, and interest rates.
Setting Up an Emergency Fund
Establishing an emergency fund is crucial for financial security. Ideally, this fund should cover three to six months’ worth of living expenses. Students can start small by setting aside a portion of their monthly income—whether from part-time jobs, allowances, or scholarships—into this fund. Having an emergency fund provides peace of mind and helps students avoid relying on credit cards or loans in times of need.
Starting Basic Investment Strategies
Investing may seem daunting for students with limited budgets, but there are several accessible strategies:
- Low-Cost Index Funds: Index funds are a popular investment choice for beginners due to their low fees and diversification. These funds track specific market indices (like the S&P 500) and allow investors to gain exposure to a broad range of stocks without needing extensive knowledge of the stock market.
- Micro-Investing Apps: Platforms like Acorns or Stash enable users to invest small amounts of money regularly. These apps often round up purchases to the nearest dollar and invest the difference, making it easy for students to start investing without needing large sums upfront.
- Robo-Advisors: For those who prefer a hands-off approach, robo-advisors provide automated investment management based on individual risk tolerance and goals. They typically require lower minimum investments and charge lower fees than traditional financial advisors.
- Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs): Students can also consider SIPs in mutual funds, allowing them to invest fixed amounts regularly (as low as $10 or $20) over time. This strategy not only helps in building wealth but also instills discipline in saving and investing.
Long-Term Benefits of Starting Early
Starting to save and invest during university years offers several long-term benefits:
- Compound Interest: One of the most significant advantages of starting early is the power of compound interest. The earlier students begin saving or investing, the more time their money has to grow exponentially. Even small contributions can lead to substantial growth over time.
- Financial Independence: By developing good financial habits early on, students can achieve greater financial independence after graduation. This independence allows them to make choices based on personal goals rather than being constrained by debt or financial insecurity.
- Building Wealth: Regular saving and investing contribute to wealth accumulation over time. Students who prioritize these practices are more likely to enter adulthood with assets that can be used for future investments, home purchases, or retirement savings.
- Reduced Financial Stress: Knowing that they have savings set aside can alleviate financial stress during university years and beyond. This peace of mind allows students to focus more on their studies and personal growth rather than worrying about finances.
- Preparation for Future Goals: Early saving and investing prepare students for future financial goals such as buying a home, starting a business, or funding further education. Having a solid financial foundation enables them to pursue these goals with confidence.
Avoiding Common Financial Mistakes
University life can be an exciting time filled with new experiences, but it also presents unique financial challenges. Many students make common financial mistakes that can lead to stress and long-term consequences. By understanding these pitfalls and implementing practical strategies, students can stay on top of their financial health and make the most of their university experience.
Common Financial Mistakes
1. Overspending on Non-Essential Items
One of the most prevalent mistakes students make is overspending on non-essential items. With newfound independence, many students find themselves tempted to indulge in dining out, shopping sprees, and entertainment expenses. These costs can quickly add up and deplete a student’s budget.
Advice: To avoid this pitfall, students should create a detailed budget that outlines their income and necessary expenses. By setting limits on discretionary spending and prioritizing needs over wants, students can maintain better control over their finances. Utilizing budgeting apps can help track spending in real-time and ensure they stay within their limits.
2. Failing to Track Expenses
Another common mistake is failing to keep track of expenses. Without monitoring where money is going, it’s easy for students to lose sight of their financial situation, leading to unexpected overdrafts or insufficient funds for essential bills.
Advice: Students should regularly review their bank statements and use budgeting tools to categorize spending. A simple practice of logging daily expenses can provide clarity on spending habits and help identify areas where they can cut back.
3. Misusing Credit Cards
Credit cards can be a double-edged sword for students. While they offer convenience and the ability to build credit, misusing them can lead to significant debt. Many students fall into the trap of using credit for non-essential purchases without considering the long-term implications.
Advice: Students should use credit cards responsibly by only charging what they can afford to pay off each month. Setting up automatic payments for the full balance can help avoid interest charges and prevent debt accumulation.
4. Ignoring the Importance of an Emergency Fund
Many students overlook the necessity of having an emergency fund. Unexpected expenses—such as car repairs or medical bills—can arise at any time, and without savings set aside, students may resort to high-interest loans or credit cards.
Advice: Students should aim to save a small percentage of their income each month to build an emergency fund. Even starting with a modest amount can provide a safety net that helps manage unforeseen costs without derailing their finances.
5. Not Researching Financial Aid Options
Some students fail to take full advantage of available financial aid options, such as scholarships, grants, and work-study programs. This oversight can result in taking out larger loans than necessary.
Advice: Students should actively research scholarship opportunities throughout their college years and apply for as many as possible. Additionally, consulting with financial aid offices can provide insights into available resources that may alleviate financial burdens.
Practical Advice for Staying on Top of Financial Health
- Create a Realistic Budget: Develop a budget that includes all sources of income and categorizes expenses into fixed (rent, tuition) and variable (food, entertainment) costs. Regularly review and adjust the budget as needed.
- Set Financial Goals: Establish both short-term (saving for a trip) and long-term (building an emergency fund) financial goals. Having clear objectives helps motivate responsible spending and saving habits.
- Educate Yourself About Personal Finance: Take advantage of personal finance courses or workshops offered by universities. Understanding basic financial principles will empower students to make informed decisions about their money.
- Utilize Technology: Use budgeting apps or online banking tools that allow tracking of expenses easily and provide alerts when nearing budget limits.
- Seek Guidance When Needed: Don’t hesitate to reach out for help from financial advisors or mentors who can provide valuable insights into managing finances effectively.
Building Credit and Financial Independence
Managing credit responsibly during university years is a critical step toward achieving financial independence. As students navigate their academic journey, understanding how to build a solid credit history can set the stage for future financial opportunities, including securing loans, renting apartments, and even landing jobs. A strong credit score not only opens doors but also can lead to lower interest rates and better terms on financial products. Here’s how students can effectively manage their credit and lay the groundwork for a secure financial future.
The Importance of Managing Credit Responsibly
A credit score serves as a reflection of a person’s creditworthiness, influencing various aspects of life beyond just borrowing money. It affects the ability to rent an apartment, qualify for insurance, and even secure employment in some cases. For university students, establishing a good credit history is essential for future financial endeavors. The earlier students start building their credit, the more they can benefit from it in the long run.
Tips for Building a Solid Credit History
- Open a Student or Secured Credit Card:
- Student credit cards are designed specifically for individuals with limited credit history and often come with lower limits to help prevent excessive debt. These cards may offer rewards like cash back on purchases, making them an attractive option for students.
- Secured credit cards require a deposit that serves as the credit limit, providing a safety net for both the issuer and the cardholder. Using these cards responsibly can help students establish a positive payment history.
- Make Timely Payments:
- Consistently paying bills on time is one of the most crucial factors affecting credit scores. Late payments can significantly harm a student’s credit history. Setting up automatic payments or reminders can help ensure that payments are made promptly.
- Keep Credit Utilization Low:
- Credit utilization refers to the ratio of current credit card balances to total available credit. Keeping this ratio below 30% is generally recommended to maintain a healthy credit score. Students should aim to use only a small portion of their available credit and pay off balances in full each month.
- Monitor Your Credit Score:
- Regularly checking your credit report helps track your progress and identify any discrepancies or unauthorized charges. Students can access free annual credit reports through AnnualCreditReport.com, which allows them to stay informed about their credit status.
- Consider Becoming an Authorized User:
- If possible, students can ask a parent or guardian to add them as an authorized user on their existing credit card account. This strategy allows students to benefit from the primary account holder’s positive payment history without being solely responsible for payments.
- Explore Credit-Builder Loans:
- Credit-builder loans are designed specifically to help individuals establish or improve their credit scores. The loan amount is held in a secured savings account while the borrower makes monthly payments, which are reported to credit bureaus.
The Long-Term Benefits of Starting Early
Starting to build credit during university years offers numerous long-term benefits:
- Access to Better Financial Products:
- A strong credit history opens doors to better loan options with lower interest rates, which can save students substantial amounts of money over time when financing major purchases such as cars or homes.
- Improved Financial Opportunities:
- Many landlords check prospective tenants’ credit scores as part of the rental application process. A good score increases the likelihood of securing desirable housing.
- Lower Insurance Premiums:
- Insurers often use credit scores as part of their risk assessment process; thus, individuals with higher scores may qualify for lower premiums on auto and renters insurance.
- Career Advantages:
- Some employers review candidates’ credit histories as part of the hiring process, particularly in finance-related fields. A solid credit score can enhance employability and demonstrate responsibility.
- Financial Independence:
- Building good credit habits early fosters financial independence post-graduation, allowing graduates to make informed decisions about loans, investments, and other financial commitments without being overly reliant on others.
Conclusion
Navigating the financial landscape of university life is a multifaceted endeavor that requires students to be proactive and informed. Throughout this discussion, we have explored several key areas essential for achieving financial success during and after university.
Understanding financial aid options is crucial for minimizing debt and maximizing available resources; budgeting effectively helps students manage their expenses and prioritize their financial goals. Furthermore, managing loans responsibly ensures that students can navigate their financial obligations without falling into debt traps.
Networking through finance associations provides invaluable opportunities for students to connect with industry professionals, gain insights, and enhance their financial literacy. Engaging with these organizations not only enriches the academic experience but also lays the groundwork for future career success. Finally, improving financial literacy equips students with the knowledge and skills necessary to make informed decisions about their finances, paving the way for long-term stability.
As students embark on their university journeys, it is vital to be proactive about their finances. Taking control of financial responsibilities early on will set them up for success after graduation, allowing them to transition smoothly into the workforce or further education without the burden of overwhelming debt or poor financial habits.
Call to Action
We encourage all students to start planning their finances early. Take advantage of available resources such as financial aid offices, personal finance workshops, and online budgeting tools. By developing a solid understanding of financial principles and actively managing their finances, students can create a strong foundation for their future. Remember, the choices made today regarding budgeting, saving, investing, and building credit will have lasting impacts on your financial well-being. Start your journey toward financial independence now—your future self will thank you!